- April 6, 2015
- Posted by: Wevio
- Category: Development, Wevio Blog

What Is SSL?
SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer. SSL is a standard security technology for establishing an encrypted link between a server (website) and a client(web-browser), allowing you to transmit private data online.
SSL allows sensitive information such as credit card numbers, social security numbers, and login credentials to be transmitted securely. Normally, data sent between browsers and web servers is sent in plain text and creates vulnerable access points. If an attacker is able to intercept all data being sent between a browser (client) and a web server they can see and use that information.
With the SSL, vulnerable access situations can be avoided. This article explains how SSL protect data transmitting between web browser and Server.
How SSL Works?
SSL Certificates have a key pair: a public and a private key. These keys work together to establish an encrypted connection. The certificate also typically contain subject, the domain name, company name, address, city, state and country.
To get a certificate, you must create a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) on your server. This process creates a private key and public key on your server. The CSR data file that you send to the SSL Certificate issuer (called a Certificate Authority or CA) contains the public key. The CA uses the CSR data file to create a data structure to match your private key without compromising the key itself. The CA never sees the private key.
Once you receive the SSL Certificate, you install it on your server. You also install a pair of intermediate certificates that establish the credibility of your SSL Certificate by tying it to your CA’s root certificate. The instructions for installing and testing your certificate will be different depending on your server.
In the image below, you can see what is called the certificate chain. It connects your server certificate to your CA’s (in this case DigiCert’s) root certificate through a series of intermediate certificates.
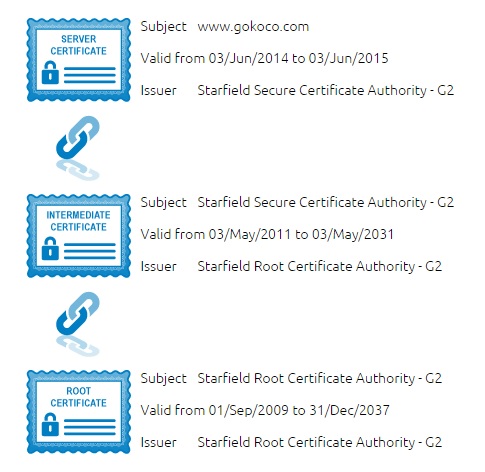
How Does the SSL Certificate Create a Secure Connection?
When a browser attempts to access a website that is secured by SSL, the browser and the web server establish an SSL connection using a process called an “SSL Handshake” (see diagram below). Note that the SSL Handshake is invisible to the user and happens instantaneously.
Essentially, three keys are used to set up the SSL connection: the public, private, and session keys. Anything encrypted with the public key can only be decrypted with the private key, and vice versa.
Because encrypting and decrypting with private and public key takes a lot of processing power, they are only used during the SSL Handshake to create a symmetric session key. After the secure connection is made, the session key is used to encrypt all transmitted data.
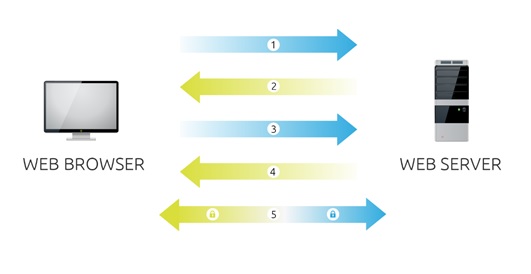
- Browser connects to a web server (website) secured with SSL (https). Browser requests that the server identify itself.
- Server sends a copy of its SSL Certificate, including the server’s public key.
- Browser checks the certificate root against a list of trusted CAs and that the certificate is unexpired, unrevoked, and that its common name is valid for the website that it is connecting to. If the browser trusts the certificate, it creates, encrypts, and sends back a symmetric session key using the server’s public key.
- Server decrypts the symmetric session key using its private key and sends back an acknowledgement encrypted with the session key to start the encrypted session.
- Server and Browser now encrypt all transmitted data with the session key.
How can I tell when a site uses SSL?
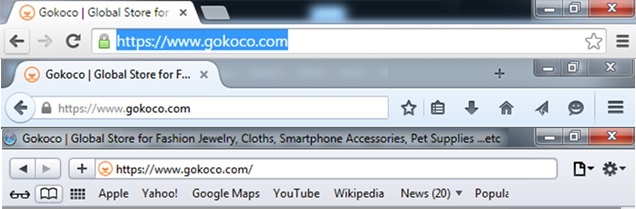
When a digital certificate is installed on a web page, users will see a padlock icon in the browser address bar. When an Extended Validation Certificates is installed on a web site, the address bar will turn green during secure sessions.
In the below image, you can see the green address bar that comes with extended validation (EV) SSL Certificates.
Services are priceless because the cost to operate the server is shared between you and these other customers. There are, however, a number of down sides, such as being slower.
What details are included in a certificate?
Certificates are issued to companies or legally accountable individuals and will typically contain the domain name, company name, address, city, state and country. It will also contain an issued date and an expiry date and contain details of the certificate authority responsible for issuing the certificate. When a browser requests a https connection to a website, it will retrieve the site’s certificate, check that it has not expired, check it is chained to a root in its certificate store, and will check it is being used by the website for which it has been issued. If it fails any of these checks, the browser will display a warning to the end user.
